Today’s Google search results are quite different from what they were ten years ago.
What was once a list of webpages now contains featured snippets, knowledge panels, related searches and predictive autocomplete functionality to help the user.
If you want to implement a successful SEO strategy for your own website, you need to have a basic understanding of how these features work.
Although Google is unlikely to ever give us an explanation of how their search algorithm works, a recent blog post by their Public Liaison for Search, Danny Sullivan sheds some light on the decisions Google makes when displaying search results.
Here’s the important stuff.
In the spotlight: featured snippets
Ask Google a question, and the websites it suggests will probably be moved down to make way for a more immediate answer.
These are known as featured snippets, and sometimes referred to as ‘ranking zero’ in Google.
A featured snippet is a piece of content pulled from a webpage by Google based on the assumption that it provides the fastest answer to your question.
Featured snippets have received their fair share of criticism, with some believing they prevent searchers from ever visiting the website from which they’re pulled.
Despite this, if your website is selected for a featured snippet, it can be even more valuable than landing the number one search spot.
It’s important to note that a number one search position and featured snippet aren’t intrinsically linked; you could achieve the top position for a keyword yet have a competitor grab the featured snippet.
This is because Google uses an entirely different method for selecting featured snippets. They’ve published their standards for selecting them, although there are absolutely no guarantees you’ll be featured if you follow them to the letter - it’s just good practice to do so!
The secret sauce: organic results
The process of ranking organic search results on Google has changed considerably. In fact, according to Sullivan, over 3,200 changes have been made to the algorithm in the last twelve months alone.
It used to be the case that you could achieve a high position on google by simply adding relevant long-tail keywords to web pages, but that approach no longer works effectively.
The algorithm Google uses to rank organic results is a closely-guarded secret, but as any successful digital marketer knows, it’s important to keep in mind that search constantly changes. As such, staying up-to-date with the latest trends and SEO features is vitally important.
Equally, Google’s algorithms aren’t perfect, therefore if you spot something is wrong, you can report it to Google to aid their efforts in refining the platform.
Quick facts: the Knowledge Graph
Search for a famous person on Google, and you’ll probably encounter the Knowledge Graph.
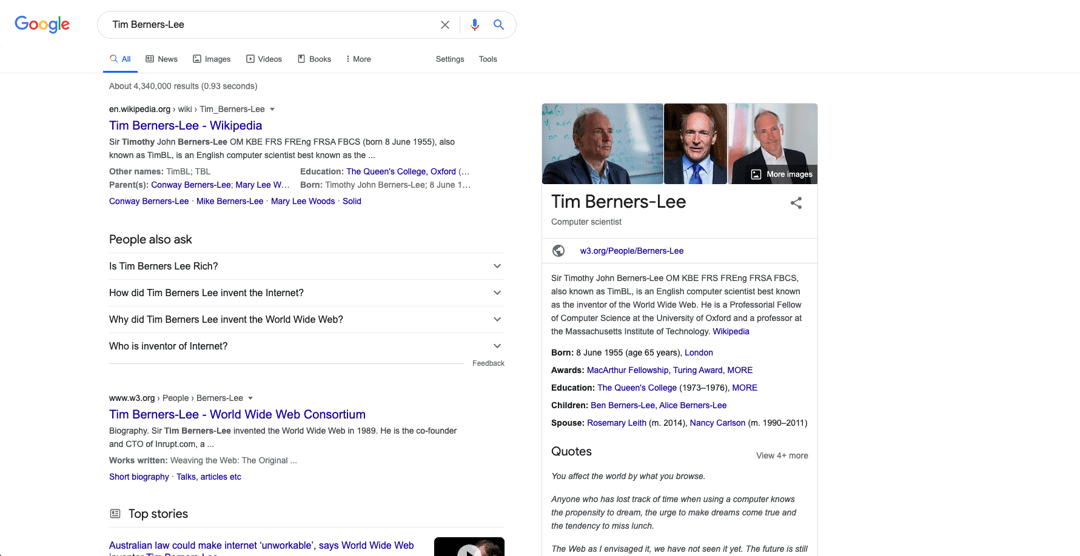 Placed on the right-hand side of search results, this is essentially a quick fact box which Google thinks might be useful, based on the search term. They pull this information from ”information gathered from the web, structured databases, licensed data and other sources”.
Placed on the right-hand side of search results, this is essentially a quick fact box which Google thinks might be useful, based on the search term. They pull this information from ”information gathered from the web, structured databases, licensed data and other sources”.
Just like featured snippets, the knowledge graph doesn’t work from Google’s ranking system. And, because it looks for information in databases, it’s unlikely to pull anything from your highly-optimised blog post.
For this reason, it’s best not to focus any effort trying to appear in the knowledge graph - your SEO time is far better invested in obtaining good organic search traffic and potentially grabbing a featured snippet.
The unthinkable: de-indexing
Google rarely de-indexes a page entirely, but they do have standards for penalising certain listings.
For instance, if a featured snippet violates their publishing standards, it will be removed, but the page is likely to remain indexed in search results.
Despite this, there are a couple of instances where a de-indexing might occur:
- By law:
any pages that violate copyright infringement or child abuse laws are removed from Google’s index. - Violation of Google’s policies:
Google has policies in place to protect sensitive personal information, and in certain instances will de-index pages that violate them.
In the latter instance, Google sometimes removes results for specific search phrases, such as someone’s name or anything else that relates to them.
The good news? If you notice your search rankings have dropped significantly or entirely, it’s unlikely you’ve been de-indexed by Google - you just need to rethink your SEO strategy.
Wrapping up
Even the best SEO professionals in the world are sometimes stumped by Google’s ever-changing approach to search, but as Danny Sullivan demonstrates, they do occasionally provide a window into their thinking.
There’s no foolproof method for getting to number one on Google or grabbing a featured snippet, but by keeping up-to-speed with the latest trends in SEO, you’ll gain a far better understanding of how Google views your website.